Why do you see two different types of replicating strands in the given DNA replication fork? Explain. Name of these strands.
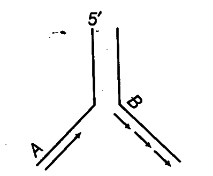
Why do you see two different types of replicating strands in the given DNA replication fork? Explain. Name of these strands.

Both the parent strands function as template strands.
On the template strand with 3’ —» 5’ polarity, the new strand is synthesised as a continuous strand. The DNA .polymerase can carryout polymerisation of the nucleotides only in 5’—» 3’ direction.
This is called continuous synthesis and the strand is called leading strand. On the other template strand with 5’ —> 3’ polarity, the new strand is synthesised from the point of replication fork, also in 5’ —» 3’ direction. But, in short fragments, they are later joined by DNA ligases to form a strand called lagging strand.