Why do you see two different types of replicating strands in the given DNA replication fork? Explain.Name these strands.
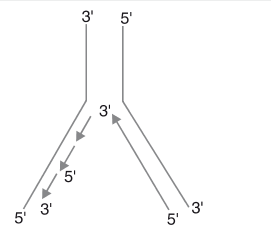
- In long DNA molecules, since the two strands of DNA cannot be separated in its entire length, the replication occur within a small opening to the DNA helix, referred to as a replication fork.
- The DNA-dependent DNA polymerases catalyses polymerization of the nucleotides only in 5’----> 3’ direction.
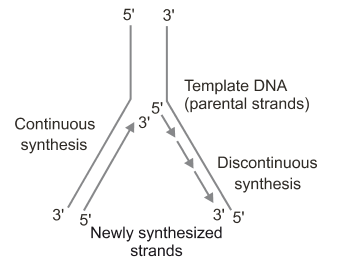
Consequently, on one of the template strands the synthesis of DNA is continuous, while on the other template strand the synthesis of DNA is discontinuous, i.e., short stretches of DNA are synthesized. - The discontinuously synthesized strands are later joined together by the enzyme DNA ligase.