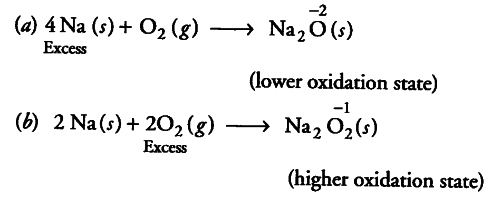Whenever a reaction between an oxidising agent and a reducing agent is carried out, a compound of lower oxidation state is formed if the reducing agent is in excess and a compound of higher oxidation state is formed if the oxidising agent is in excess. Justify this statement giving three illustrations.
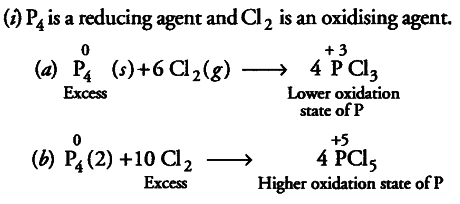
Therefore, when { P }_{ 4 } (reducing agent) is in excess,
{ PCl }_{ 3 } is formed in which oxidation state of P is + 3 and if
{ Cl }_{ 2 } (oxidising agent) is in excess,
{ PCl }_{ 5 } is formed in which oxidation state of P is + 5. Other two examples are
(ii) C is a reducing agent while {{O}_{2}} is an oxidising agent.
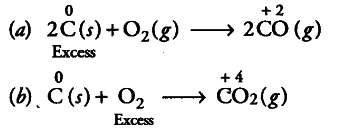
When reducing agent C is in excess, a compound CO of lower oxidation state is formed, if oxidising agent {{O}_{2}} is in excess, a compound
{{CO}_{2}} of higher oxidation state is formed.
(iii) Na is a reducing agent while {{O}_{2}} is an oxidising agent.