what metal excess defects? explain with example
1) Metal Excess:
This occurs in two ways,
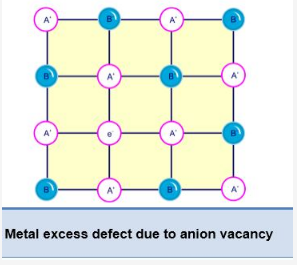
A. By anion vacancies:
-
In this defect, a negative ion is missing from its lattice site, leaving behind a hole which is occupied by an electron and maintain the electrical balance.
-
The sites which contain the electrons are trapped in the anion vacancies.
-
They are known as F-centres because they are responsible for giving colour to the crystal.
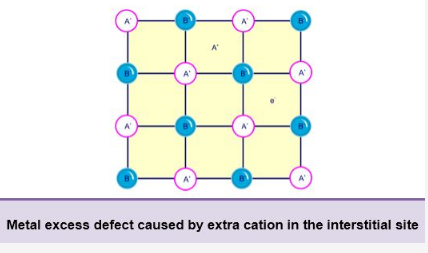
B. By the presence of extra cations in the interstitial sites:
- Metal excess defect may also cause by extra cations which occupy the interstitial sites.
- Electrical neutrality is maintained by an electron present in another interstitial site.
- This defect is found in the crystals which show Frenkel defect.
- When ZnO is heated, it loses oxygen and turns yellow.
- The excess of Zn2+ ions are trapped into the vacant interstitial sites and electrons are trapped into the neighbouring interstitial sites.
- The crystals with this type of effect act as a semiconductor as they contain some free electrons.