What is the systematic name of Mg(NO3)2, NH4ClO3, and PbO and how do you get those answers.
Concepts and reason
The IUPAC (International Union for Pure and Applied Chemistry) nomenclature:
The IUPAC nomenclature describes the systematic rules for naming inorganic compounds. In general, charged particle known as ions that will have two parts such as cation and anion.
Fundamentals
The IUPAC name of inorganic compounds is divided by two parts of a cation and anion.
The compound with negative ion is called anion.
The compound with positive ion is called cation.
The given compounds follow two rules:
For examples the simple ionic compound:
![]() = calcium fluoride
= calcium fluoride
Name of this compound is simply cation and followed by anion.
Cation with more than one positive charge can labeled with Roman numerals in parentheses.
![]() = copper(II)
= copper(II)
The Oxyanions are named with –ate of –ite.
For examples:
![]() = nitrite
= nitrite
![]() = nitrate
= nitrate
Answer:
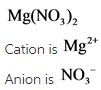
IUPAC name is Magnesium nitrate.
Explanation:
The charge of magnesium cation is always +2 and no need to specify (II) roman letter. The anion name has –ate as a suffix due to the presence of three oxygen. Hence, the given compound is magnesium nitrate.
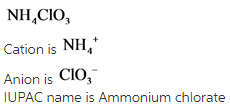
Explanation:
The charge of ammonium is always +2 and no need to specify (I) roman letter. The anion name has –ate as a suffix due to the presence of three oxygen. Hence, the given compound is Ammonium chlorate.

Explanation:
The lead forms different oxidation states, so it can be form +1, +2, etc. So, the charge PbO is +2 and need to specify (II) roman letter. The anion name has –ide as a suffix due to the presence oxygen. Hence, the given compound is Lead(II) oxide.