What is the oxidation state of each element in Mn(NO3)2?
Concepts and reason
This problem is based on the concept oxidation state.
In order to ease the understanding of redox reactions, oxidation states are assigned where some atoms lose (are oxidized) and others gain (are reduced) electrons. An oxidation state is the positive or negative charge the atom would have if the molecule was ionic.
Fundamentals
Certain rules are followed in order to assign oxidation numbers to each molecule or atom but for the given compound, the three rules followed are:
- Oxygen has -2 oxidation states except for in case of peroxides where it is -1.
- The sum of oxidation states of all atoms in a polyatomic ion is equal to the charge on the
polyatomic ion. - For a neutral molecule, the sum of individual oxidation states is 0.
Oxidation number can be calculated using the formulae.
Answer:
Oxygen is usually considered to have -2 oxygen state. In the given question, oxidation state of ![]() is to be found -2.
is to be found -2.
Explanation:
Following the rules to assign oxidation state, Oxygen has -2 oxidation state except for in case of peroxides where it is -1. In this case, oxygen does not form a peroxide.
Next considering the ligand ![]() , let the oxidation state of nitrogen be
, let the oxidation state of nitrogen be ![]() . Oxidation number for oxygen is -2. The formula is given below:
. Oxidation number for oxygen is -2. The formula is given below:
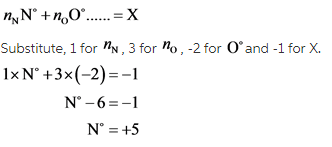
Explanation:
Following the rule that the sum of oxidation states of all atoms in a polyatomic ion is equal to the charge on the polyatomic ion, the state of nitrogen is found to be +5.
![]() is a neutral compound and the oxidation states of nitrogen and oxygen are found to be +5 and -2, respectively. Using the formulae:
is a neutral compound and the oxidation states of nitrogen and oxygen are found to be +5 and -2, respectively. Using the formulae:
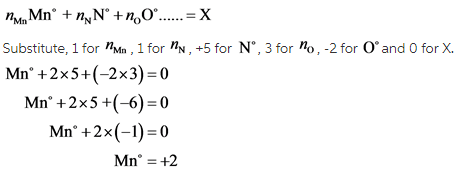

Explanation:
For a neutral molecule, the sum of individual oxidation states is 0. Since the oxidation states of Nitrogen and oxygen have already been found in previous steps, the oxidation state of manganese can be found by simple substitution.
