What is meant by ‘rusting’? With labelled diagrams describe an activity to find out the conditions under which iron rusts.
When iron is exposed to air and moisture for a very long time, it gets covered with a brown flaky substance. This brown flaky substance is called rust and the process is called rusting.
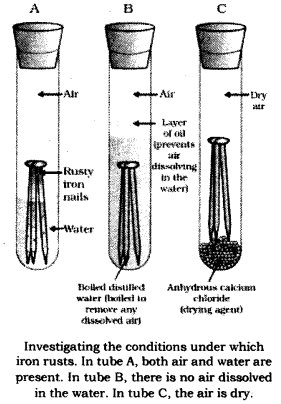
The conditions under which iron rusts can be found using the given activity.
Activity: Take three boiling tubes and label them A, B and C. Place three clean iron nails (free from rust) in each of the tube. Add water to tube A, in such a manner that some parts of the nails are exposed to air. Add water to test tube B, in such a way that the nails are completely submerged in water. Then, pour some amount of oil in the tube. Add anhydrous calcium chloride to test tube C and then seal it. Anhydrous calcium chloride absorbs all the moisture present inside the tube so that the nail is only exposed to oxygen and no moisture. Seal all the tubes with the help of rubber corks. Leave the tubes undisturbed for a few weeks and observe the changes.
Conditions for rusting of iron: It will be observed after a few weeks that the nails in tube A have rusted, while those in test tubes B and C have not.
Explanation: In tube A, both moisture and oxygen were available and the nails started rusting after two weeks.
In tube B, iron nail was only in contact with water, and oxygen was not allowed to dissolve in water because of the layer of oil. As nails did not rust even after two weeks when only water was available, it shows that rusting cannot take place if only water is available.
In tube C, only oxygen was present as anhydrous calcium chloride absorbed all the moisture present inside the boiling tube. As the nails did not rust even after two weeks when only oxygen was available, it shows that rusting cannot take place if only oxygen is available.