What happens to the demand of a good when consumer’s income changes? Explain.
The quantity of a good that the consumer demands can increase or decrease with the rise or fall in income depending on the nature of the good.
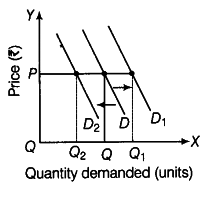
(i) Normal goods These are the goods for which the demand is directly related to consumer’s income. Other things remaining constant, demand for these goods increases in response to increase in consumer’s income and vice-versa, e.g. full cream milk, pulses, grains, etc.
The given figure illustrates the income effect in case of normal goods. When Income increases, the demand curve D shifts to right to D, and when income decreases, the demand curve D1 shifts to left to { D }_{ 2 }
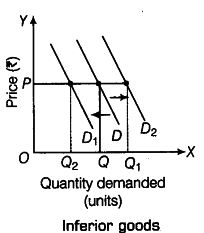
(ii) Inferior goods These are the goods for which the demand is inversely related to consumer’s income. Other things remaining constant, y, demand for these goods decreases in response to increase in income and vice-versa, e.g. coarse cereals, toned milk, etc. 0
The given figure illustrates the income effect in case of inferior goods. When income increases, the demand curve D shifts to left to${ D }_{ 1 }$ and when income decreases, the demand curve D shifts to right to D2
In case of normal goods, income effect is positive while in case of inferior goods, income effect is negative.