what are cathode ray experiment and anode ray experiment
Discovery of Electrons
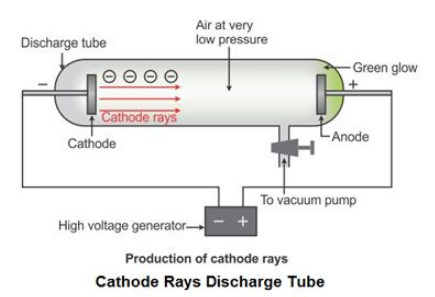
Discovery of Cathode Rays
-
The study of atomic structure and sub-atomic particles was initiated by the discovery of the discharge tube. Experiments on the discharge tube were first conducted in 1878 by an English physicist, William Crookes .
-
When a high-voltage electric current is passed through the discharge tube containing a gas at a very low pressure, a green fluorescence is seen coming out of the other end of the discharge tube.
-
This fluorescence is the result of rays emitted from the cathode (negative plate) towards the anode (positive plate) in the discharge tube. Hence, these rays are called cathode rays .
-
Later, J. J. Thomson studied the characteristics and the constituents of cathode rays.
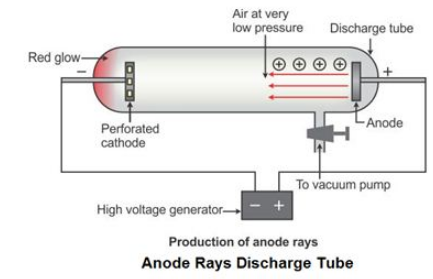
Discovery of Protons -
A German scientist, E. Goldstein modified the discharge tube and passed an electric current through it.
-
He found that positively charged rays were emitted from the anode in the discharge tube. These rays were called canal rays .
-
When an electric field was applied, these rays deflected towards the negatively charged plate. Thus, Goldstein concluded that an atom contains positively charged particles along with the electrons.
-
These positively charged particles were named as protons by a British scientist, Ernest Rutherford.
-
Canal rays were also called anode rays because they emitted from the anode (electrode connected to the positive terminal of a high-voltage source) in the gas discharge experiments using perforated cathode.