The conjugate acid of HPO42
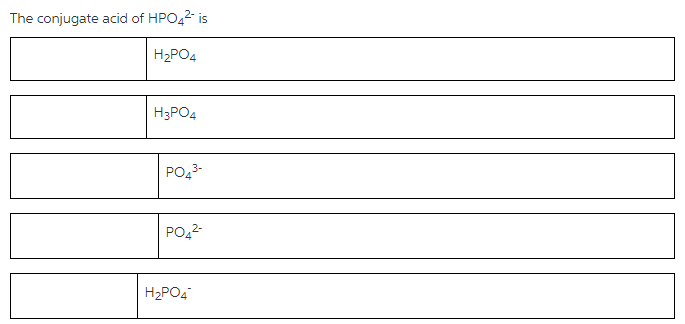
Concepts and reason
The concept used to solve this problem is based on the conjugate acid and conjugate base.
The conjugate acid base pair differs by one proton.
Fundamentals
According to the Bronsted-lowery theory, a conjugate acid is a species which is formed by reaction of proton with a base. a conjugate base is a species which is formed when acid loses a proton.
The reaction representing the formation of conjugate acid and conjugate base is as follow:
![]()
Acid donates hydrogen ion and base is the acceptor of proton. The conjugate acid base pair differs by one proton. Conjugate acid is formed when a hydrogen ion is added to the base. Whereas, the conjugate base is formed when an acid donates its proton (hydrogen ion).
Therefore, the base, hydrogen phosphate ion reacts with a proton to form a conjugate acid.
According to Bronsted-Lowry definition, conjugate acid is formed when a base accepts a hydrogen ion. Moreover, conjugate base is formed when an acid loses a proton.
The reaction of hydrogen phosphate ion with a proton to form its conjugate acid, dihydrogen phosphate ion is as follow.
![]()

![]()
Dihydrogen phosphate ion is conjugate acid of hydrogen phosphate ion which is formed by adding a proton to hydrogen phosphate ion. Conjugate acid of ![]() is
is ![]() .
.