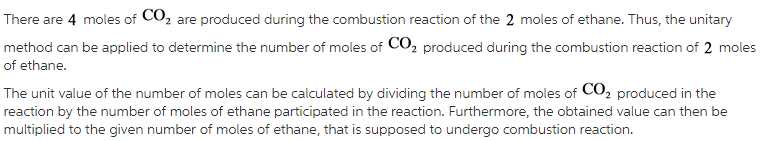The combustion of ethane (C2H6) produces carbon dioxide and steam: 2C2H6(g) + 7O2(g) 4CO2(g) + 6H2O(l) How many moles of CO2 are produced when 5.20 mol of ethane are burned in an excess of oxygen?
Concepts and reason
The given problem can be solved based on the concepts of the unitary method. The unitary method is applied to find out the value of any entity for which the single unit value is known. In this approach, the required variable value is multiplied to the single unit value.
Fundamentals
The reaction of a hydrocarbon compound with oxygen, which results in the production of the water and the carbon dioxide is referred to as combustion reaction.
The unitary method is applied to find out the value of any entity for, which the single unit value is known. In this approach, the required variable value is multiplied to the single unit value.
Answer:
The chemical reaction mentioned below, describing the combustion of ethane, ![]() is a balanced chemical reaction:
is a balanced chemical reaction:
![]()
In the above chemical reaction, ‘g’ is used to denote the gaseous nature of the species participating in the chemical reaction.
Explanation:
The number of different atoms participating in the reaction as the reactant and the number of atoms of the formed as a product are same. The number of Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms in both sides of the reaction are 4, 12 and 14 respectively.
Explanation: