The colour of potassium dichromate solution changes with change in pH of the solution. Explain.
The solution of potassium dichromate is orange while that of chromate is yellow.
When dichromate is dissolved in water, following equilibrium exist:
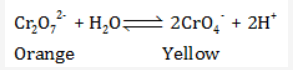
The equilibrium will shift to left in excess of H+ ions. Hence the more acidic the solution, the more the equilibrium is shifted to the left towards the dichromate ion and the colour of the solution is orange.
When we add OH- ion in solution (increasing the pH), it will react with H+ ion present in solution increasing the concentration of H2O.
As the concentration of H2O will increase, the equilibrium will shift towards right and the concentration of chromate ions will increase and the colour of the solution will change to yellow.