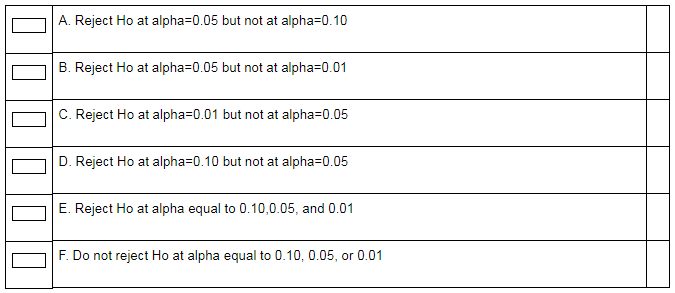
Suppose you conduct a test and your p-value is equal to 0.016. What can you conclude?
Concepts and reason
Null hypothesis: The null hypothesis states that there is no difference in the test, which is denoted by ![]() Moreover, the sign of null hypothesis is equal (=), greater than or equal
Moreover, the sign of null hypothesis is equal (=), greater than or equal ![]()
Alternative hypothesis: The hypothesis that differs from the ![]() is called alternative hypothesis. This signifies that there is a significant difference in the test. The sign of alternative hypothesis is less than (<), greater than (>), or not equal
is called alternative hypothesis. This signifies that there is a significant difference in the test. The sign of alternative hypothesis is less than (<), greater than (>), or not equal ![]()
P-value: The probability of getting the value of the statistic that is as extreme as the observed statistic when the null hypothesis is true is called as P-value.
Fundamentals
Rejection rule based on p-value:

Answer:

The p-value and the level of significance are compared to check if the null hypothesis is rejected or not.
If p-value is greater than the level of significance then the null hypothesis is not rejected otherwise it is rejected.

![]()
The p-value and the level of significance are compared to check if the null hypothesis is rejected or not.
If p-value is greater than the level of significance then the null hypothesis is not rejected otherwise it is rejected.
![]()