Some time ago formation of polar stratospheric clouds was reported over Antarctica. Why were these formed? What happens when such clouds break up by warmth of sunlight?
In summer season, nitrogen dioxide and methane react with chlorine monoxide and chlorine free radicals forming chlorine sinks, preventing much ozone depletion, whereas in winters, special type of clouds, called the polar stratospheric clouds are formed over Antarctica.These polar stratospheric clouds provide surface on which chlorine nitrate gets hydrolysed to form hypochlorous acid. It also reacts with hydrogen chloride to give molecular chlorine.
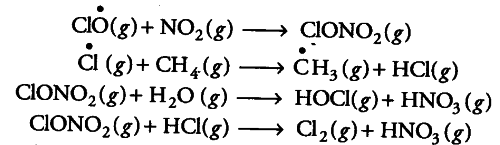
When sunlight returns to the Antarctica in the spring, the sun’s warmth breaks up the clouds and HOCl and {{Cl}_{2}} are photolysed by sunlight.
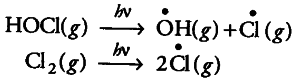
The chlorine radicals thus formed, initiate the chain reaction for ozone depletion.