Rank these compounds by their expected boiling point.
Concepts and reason
Boiling point of an alkane depends on its structure and molecule mass. Boiling point of alkanes with same molecular mass varies with their structure.
The stronger the intermolecular forces, the higher will be boiling point. Among the intermolecular forces, hydrogen bonds are strong and London dispersion forces are very weak.
Fundamentals
Due to greater surface area contact in straight chain alkane they will have greater van der Waals forces and high boiling point.
Boiling point of alcohols increases, as the hydrogen bonding increases.
Answer:
The structures are as follows:
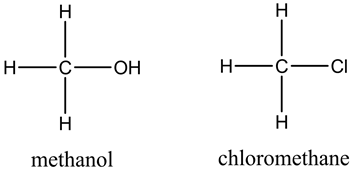
Here, methanol exhibits hydrogen bonding whereas chloromethane exhibits dispersion forces and dipole-dipole interactions. So, methanol has high boiling point than chloromethane.
The structures are as follows:
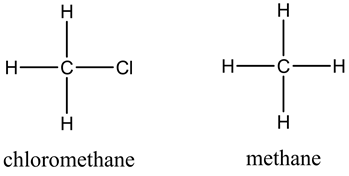
The order of boiling points from highest to lowest is ![]()
Here, chloromethane exhibits dispersion forces and dipole-dipole interactions whereas methane exhibit only dispersion forces. So, chloromethane has high boiling point than methane.