rank these compounds by boiling point from highest to lowest boiling point: pentane, neopentane, hexane.
Concepts and reason
Boiling point of an alkane depends on its structure and molecule mass. Boiling point of alkanes with same molecular mass varies with their structure. A straight chain alkane will have higher boiling point than a branched-chain alkane of same molecular mass.
A straight alkane with greater molar mass will have higher boiling point than a straight chain alkane with lower molar mass.
Fundamentals
A straight chain alkane will have greater surface area contact than a branched-chain alkane. Due to greater surface area contact in straight chain alkane they will have greater van der Waals forces and high boiling point.
Answer:
The structures of pentane and neopentane are as follows:
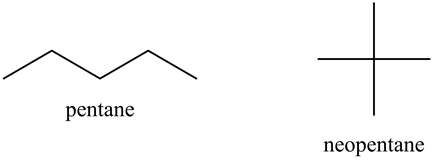
Pentane is straight chain alkane and neopentane is branched chain alkane with same molar mass.
The van der Waals forces of attraction in pentane are greater than van der Waals force of attraction than neopentane. So boiling point of pentane is greater than boiling point of neopentane, that is boiling point (pentane) > boiling point (neopentane).
Following are structures of hexane and pentane:
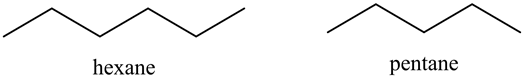
Both pentane and hexane are straight chain alkanes. Hexane will have greater boiling point than pentane.
Boiling point (BP) from highest to lowest is:
BP (hexane) > BP (pentane) > BP (neopentane)
Molar mass of hexane is greater than molar mass of pentane. Hexane will have greater van der Waals forces of attraction than pentane. So boiling point of hexane is greater than boiling point of pentane, that is boiling point (hexane) > boiling point (pentane).