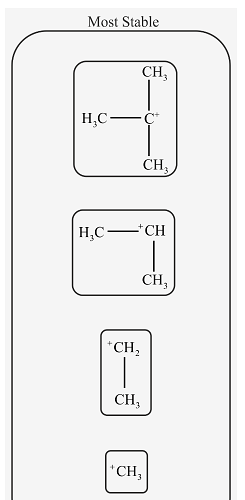
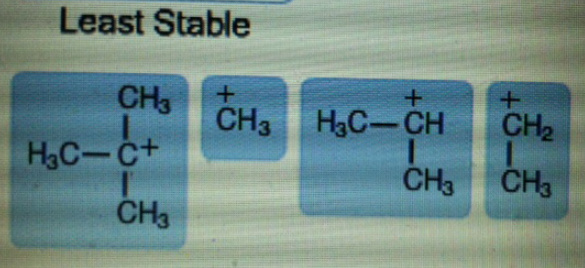
Rank the following carbocations in order of decreasing stability.
Concepts and reason
The concept used to solve this problem is based on strength of carbocation.
A carbocation is an organic molecule in which there are three bonds and one positive charge present on the carbon atom.
Fundamentals
The stability of carbocation is based on the type of carbocation.
Primary carbocations are the carbocation in which there is only one alkyl or aryl group is attached to carbon atom bearing a positive charge.
Secondary carbocations are the carbocation in which there are two alkyl or aryl groups are attached to carbon atom bearing a positive charge.
Tertiary carbocations are carbocations in which there are three alkyl or aryl groups attached to carbon atom bearing a positive charge.
Answer:
The mention structures in the question are primary, secondary and tertiary as follow.
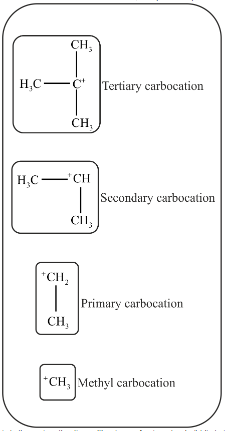
In tertiary carbocation, the positive charge of carbon atom is distributed among three methyl groups. In secondary carbocation, positive charge is distributed among two methyl groups.
More the positive charge is spread out, more stable is the carbocation. Therefore, tertiary carbocation is more stable than secondary carbocation.
Explanation:
Carbon is more electronegative than hydrogen. Thus, alkyl group present on carbon has a slightly negative charge. So, more the number of alkyl groups are present on carbon, more the positive charge is spread out. Therefore, more stable is the carbocation.
In secondary carbocation, positive charge is distributed among two methyl groups. In primary carbocation, positive charge is distributed among one methyl group. In methyl carbocation, there are only 3 hydrogen atoms attached to carbon bearing a positive charge. So, distribution of charge in methyl carbocation is least.
Therefore, Secondary carbocation is more stable than primary and methyl carbocation.
Explanation:
The stability of carbocation depends on the number of alkyl groups attached to the carbon atom bearing a positive charge. More the number of alkyl groups attached to carbon, more the positive charge is spread out and hence more stable is the carbocation.