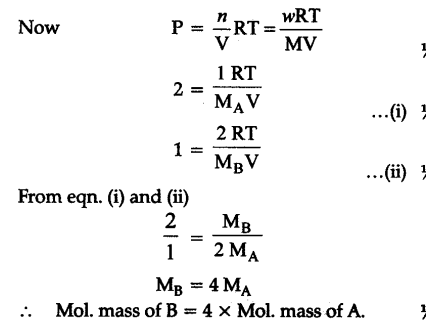Pressure of 1 g of an ideal gas ‘A’ at 27°C is found be 2 bar. When 2 g of another ideal gas B is introduced in the same flask at the same temperature the pres¬sure become 3 bar. Find a relationship between then- molecular masses
Pressure of 1 g of an ideal gas A at 27°C = 2 bar
Pressure of 2 g of another ideal gas B in same flask = 3 bar
.-. Pressure due toB = 3- 2 = 1 bar