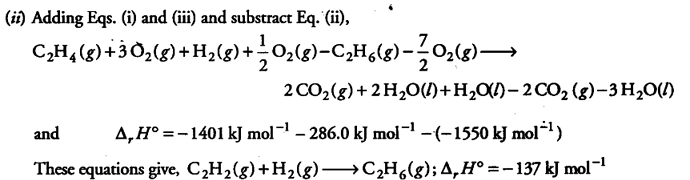(i) An athlete is given 100 g of glucose of energy equivalent to 1560 kJ. He utilises 50% of this gained energy in the event. In order to avoid storage of energy in the body, calculate the weight of water that would need to perspire. The enthalpy of vaporisation of water is 44 kJ /mol.
(ii) Compound with carbon-carbon double bond, such as ethylene, C_{2}H_{4}, add hydrogen in a reaction called hydrogenation,
C_{2}H_{4} + { H }_{ 2 } -------->
C_{2}H_{6}
Calculate enthalpy change for the reaction, using the following combustion data