Market for a product is in equilibrium, supply of the product ‘decreases’. Explain the chain of effects of this change till the market again reaches equilibrium. Use diagram.
Demand curve, remaining unchanged, if there is decrease in supply, supply curve and equilibrium point will shift leftwards. As a result, equilibrium price will increase but equilibrium quantity will decrease.
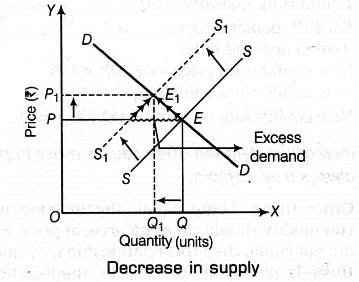
In the given diagram, actual demand curve DD and actual supply curve SS intersect at point E (i.e.
. equilibrium point).
At this point, actual quantity demanded is OQ. Due to decrease in supply, new supply curve intersects the demand curve at new equilibrium point. Consequently the price rises and equilibrium quantity falls.