How is equilibrium price of commodity determined? What happens if the market price is more than the equilibrium price?
The equilibrium price is the price at which market demand and market supply are equal to each other as shown in following schedule and diagram:
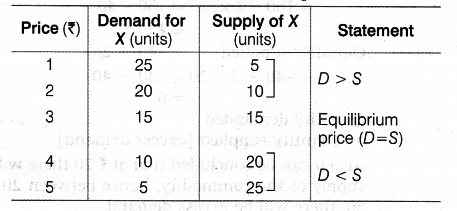
When price is Rs. 5, the supply of commodity X is 25 units. With a view to increase their sales, the seller will reduce the price.
At Rs. 3 demand and supply of commodity X becomes equal’to 15. Hence, Rs. 3 is the equilibrium price.
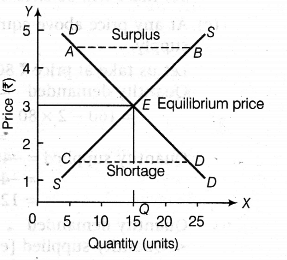
In the given figure, demand and supply of commodity Zare equal at E point. Equilibrium price is OP at Rs.3.
If market price is Rs 4, the demand will be (10) less than supply (20), excess supply will force the market price to slide down till the equilibrium between supply and demand is struck. Thus, equilibrium price will be restored in the free market economy.