(a) How is a toroid different from a solenoid ?
(b) Use Ampere’s circuital law to obtain the magnetic field inside a toroid.
© Show that in an ideal toroid, the magnetic field (i) inside the toroid and (ii) outside the toroid at any point in the open space is zero.
(a) A toroid can be viewed as a solenoid which has been bent into a circular shape to close on itself.
(b) 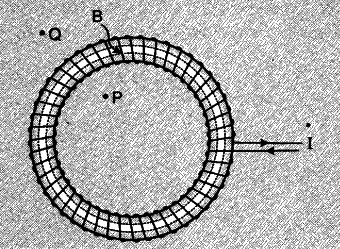

For the magnetic field at a point S inside a Toroid we have
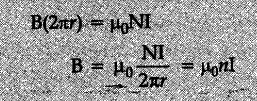
© For the loop 1, Ampere’s circuital law gives
B1 = 0
Thus the magnetic field, in the open space inside the toroid is zero.
But from the section cut, we see that the current coming out of the plane of the paper, is cancelled exactly by the current going into it.