How bond energies and bond lengths of molecule helps us in predicting their chemical properties ? Explain with examples.
- Bond length: Bond length or bond distance is the equilibrium distance between the nuclei of two atoms which form a covalent bond.
- Bond energy : Bond energy or bond dissociation energy is the energy needed to break a covalent bond between two atoms of a diatomic covalent compound in its gaseous state.
- If the nature of the bond between the same two atoms changes, the bond length also changes. For example, the bond lengths between two carbon atoms are :
C-C > C = C > C = C - Thus the various bond lengths between the two carbon atoms are in ethane 1.54 \overset { 0 }{ A }, ethylene 1.34 \overset { 0 }{ A }, acetylene 1.20 \overset { 0 }{ A }.
- The bond lengths between two oxygen atoms are in $H _{ 2 }$$O _{ 2 } (O - O) is 1.48 \overset { 0 }{ A }$ and in O _{ 2 } (O = O) is 1.21 \overset { 0 }{ A }.
- Observe the table.
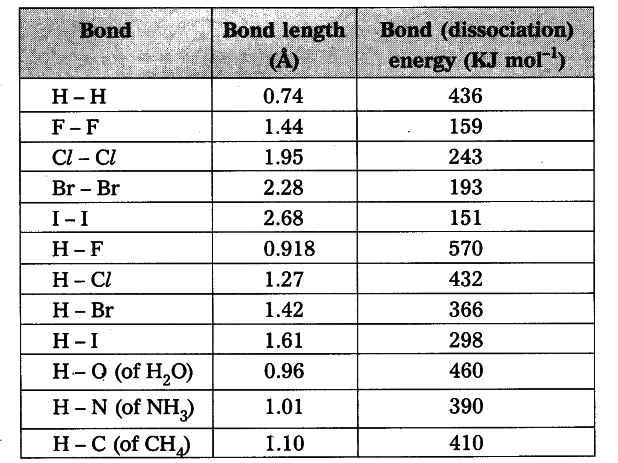
- When bond length decreases, then bond dissociation energy increases.
- When bond length increases, then bond dissociation energy decreases.
- Bond length of H - H in H _{ 2 } molecule is 0.74 \overset { 0 }{ A } and its bond dissociation energy is 436 kJ/mol, whereas bond length of F - F in F _{ 2 } molecule is 1.44 \overset { 0 }{ A } and its bond dissociation energy is 159 kJ/mol.
- Melting and boiling points of substances also can be determined by this bond energies and bond lengths.