Give a brief description of the principles of the following technqiues taking an example in each case : (a) Crystallisation, (b) Distillation,
© Chromatography.
(a) Crystallisation : (1) The process by which an impure compound is converted into its crystals is known as crystallisation.
(2) The impure substance is dissolved in a suitable solvent in which it is sparingly soluble at room temperature.
(3) The solution is concentrated to get nearly a saturated solution. When this saturated solution is cooled, crystals of the pure substance will separate out. Impure sugar is purified by this method.
(b) Distillation : (1) Distillation involves conversion of a liquid into vapours by heating followed by condensation of the vapours thus produced by cooling.
(2) If a mixture of two liquids having different boiling points are to be separated then that liquid will be received first in the reciever whose B.E is less or vapour pressure is more.
(3) A mixture of toluene and hexane can be sepa¬rated by this method.
© Chromatography:
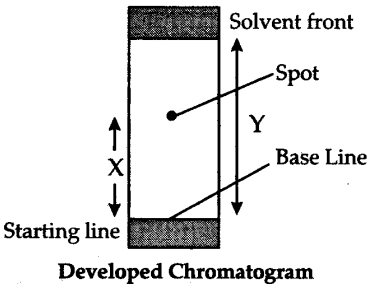
(1) The technique of separating the components of a mixture in which separation is achieved by the differential movement of individual components through a stationary phase under the influence of a mobile phase.
(2) The stationary phase can be either a solid or tighly bound liquid on a solid support while the mobile phase can be either liquid or a gas.
(3) There are two types of adsorption chromatography :
(i) Column chromatography
(ii) Thin layer chromatography
The paper strip so developed is called the chromatogram.