For which of the following mixtures will Ag2SO4(s) precipitate?
1. 150.0 mL of 0.10 M Na2SO4(aq) and 5.0 mL of 0.20 M AgNO3(aq)
2. 150.0 mL of 0.10 M Na2SO4(aq) and 5.0 mL of 0.30 M AgNO3(aq)
3. 150.0 mL of 0.10 M Na2SO4(aq) and 5.0 mL of 0.40 M AgNO3(aq)
4. 150.0 mL of 0.10 M Na2SO4(aq) and 5.0 mL of 0.50 M AgNO3(aq)
Concepts and reason
The solubility product for the reaction is equilibrium constant where the solid ionic compound dissociates into its ions in a solution. The solubility product is denoted as ![]() . The solubility product value relates to the saturated solution and indicates the precipitate level of the compound. The formation precipitation starts when ionic product exceeds the solubility product.
. The solubility product value relates to the saturated solution and indicates the precipitate level of the compound. The formation precipitation starts when ionic product exceeds the solubility product.
Fundamentals
The solubility product value of the compound depends on the concentrations of its ions in a solution.
Example: AB is a solid ionic compound.
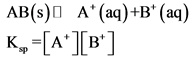
Precipitation: If the solubility product value is lesser than the concentration of the ions present in the solution, the compound precipitates in the solution.
Answer:
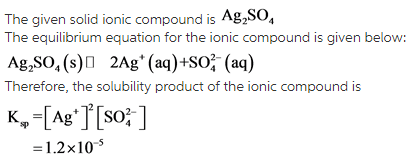
The equilibrium equation has been written for the given solid ionic compound![]() , and the solubility product has been derived from the equilibrium equation.
, and the solubility product has been derived from the equilibrium equation.
For the mixture,
