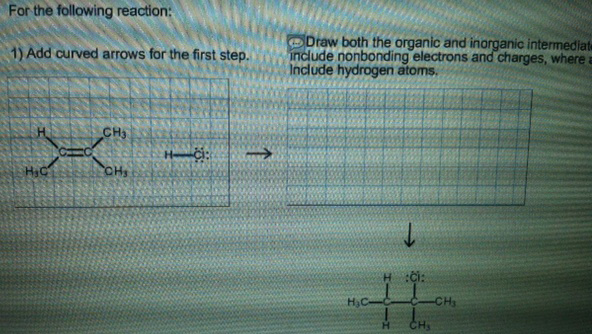
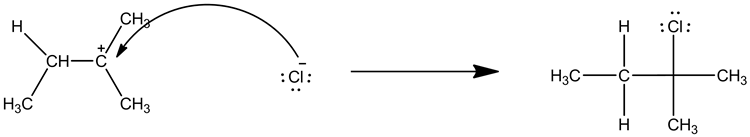For the following reaction:
1. Add curved arrows for the first step.
2. Draw both the organic and inorganic intermediate species.
Include non-bonding electrons and charges, where applicable. Include hydrogen atoms.
Concepts and reason
This problem is based on the concept of hydrogen halide addition of alkenes.
An alkene on reaction with hydrochloric acid results in formation of chloro-alkane. This reaction is carried out on the basis of stability of intermediate species. More stable intermediate regulates the mechanism.
Fundamentals
Alkene first attacks on the hydrogen ion (proton) in order to form a carbocation and then the halogen anion attacks on the carbocation in order to form haloalkane.
Answer:
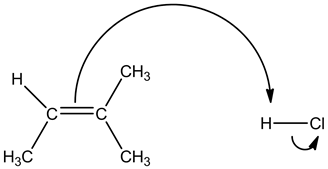
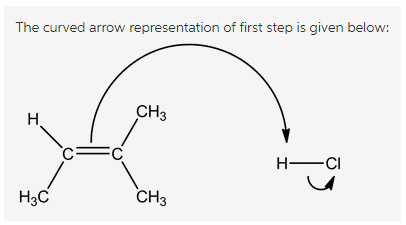
Attack of alkene on hydrogen ion is shown below:
Explanation:
The double bond due to its high electron density attacks on the electron poor hydrogen atom. Halogens are highly electronegative which makes the attached hydrogen atom more acidic.
The structure of intermediate species and their conversion to the product is as follows:

Explanation:
When alkene undergoes a protonation reaction, there is formation of cation takes place which is based on stability of carbocation. Hydrogen is attached to the olefin carbon which has more number of hydrogen atoms this results in the formation of more stable carbocation.