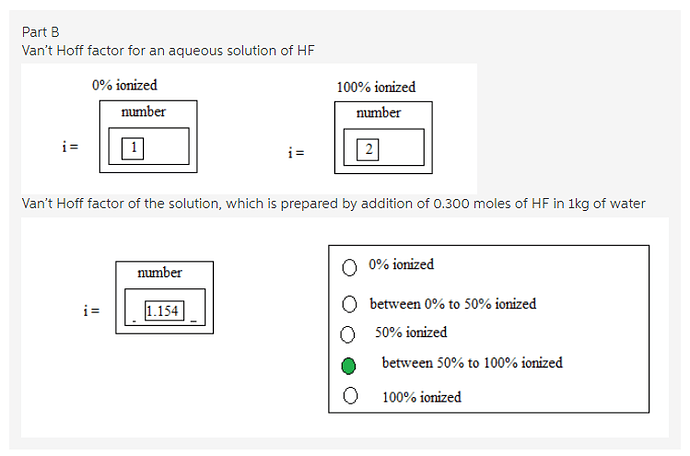
For an aqueous solution of HF, determine the van’t Hoff factor assuming…

Concepts and reason
Colligative properties: Colligative properties are properties that depend on the ratio of solute particles to solvent particles in a mixed volatile and non-volatile solution. These properties do not depend on the nature of the solute particles. Colligative properties are given below.
- Relative lowering of vapor pressure
- Boiling point elevation
- Freezing point depression
- Osmotic pressure
Fundamentals
-
Elevation of boiling point: Boiling point for a pure substance is increased by adding non-volatile solute to it.

-
Freezing point depression: Freezing point for a pure substance is lowered by adding insoluble substances to it.

Van’t Hoff factor for the substance is the number of ions present in that solution.
Answer:
Given solution is aqueous solution of HF.
If the solution is not ionized (0% ionization), then the van’t Hoff factor value is 1 since only HF molecules are present in the solution.
If the solution is fully ionized (100% ionization), then the van’t Hoff factor value is 2 since there are two ions ![]() that are present in the solution.
that are present in the solution.
Therefore, ‘i’ value is 1 for 0% ionization and ‘i’ value is 2 for complete ionization.
Explanation:
Van’t Hoff factor values have been found for completely ionized condition and non-ionized condition of aqueous solution of HF. Non-ionized aqueous solution of HF has only HF molecules in the solution, so the van’t Hoff factor value is 1. Completely ionized solution has two ions ![]() in the solution, so the van’t Hoff factor is 2.
in the solution, so the van’t Hoff factor is 2.
Given reaction condition is written below.
A solution is prepared by dissolving 0.0300 mole of HF in 1.00kg of water.
Cryoscopic constant for water is 1.86
Freezing point of the solution is -0.06440C
Depression in freezing point value is shown below.
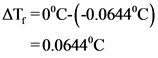
Molality of the solution is calculated below.

Van’t Hoff factor for the solution is calculated below.
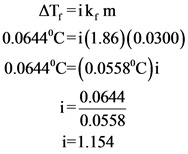
Therefore, van’t Hoff factor for the given solution is 1.154
It is clear from the van’t Hoff factor that the solution is ionized more than 50%.
Explanation:
Van’t Hoff factor has been found for the given solution by using the colligative property depression in freezing point. Van’t Hoff factor is more than 1, which means that the solution is more than 50% ionized since the complete ionization is 2.