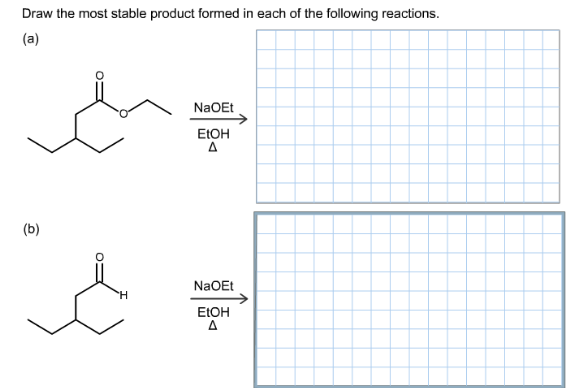
Draw the most stable product formed in each of the following reactions.
Concepts and reason
A condensation reaction is a type of chemical reaction, which has a huge importance in organic synthesis.
Aldol condensation:
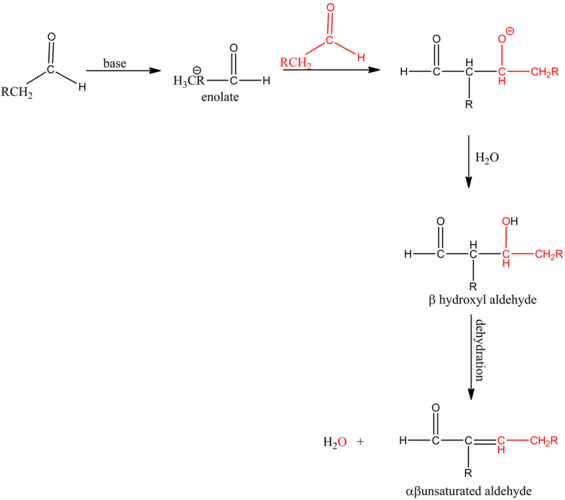
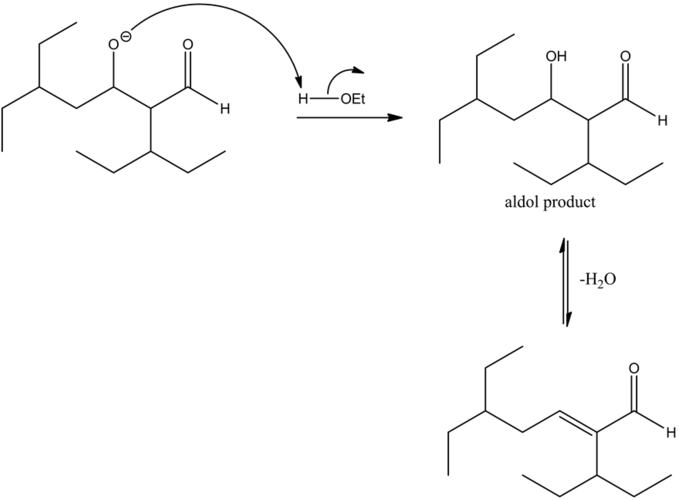
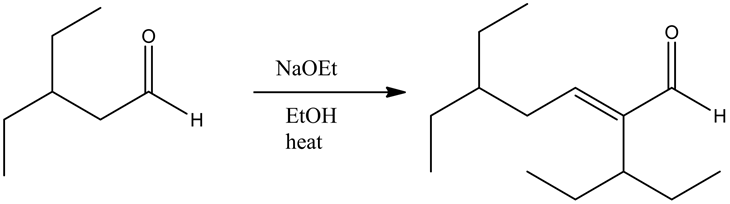
An aldol condensation reaction is a type of condensation reaction in which two aldehydes have a α-hydrogen atom each, reacting with one another to form a product called aldol.
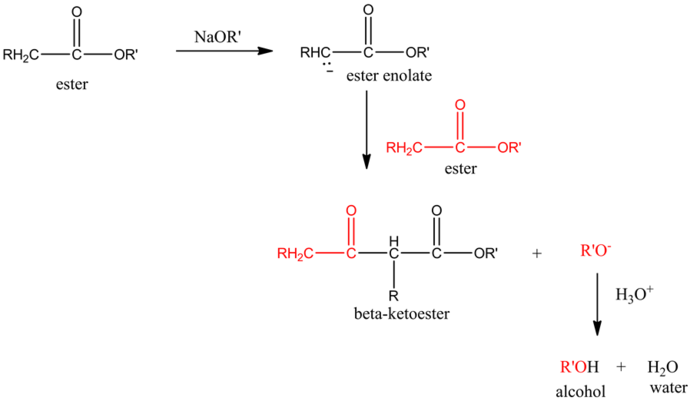
Claisen Condensation:
Claisen condensation is similar to aldol condensation. An ester which has alpha hydrogen atoms undergoes condensation reaction.
Fundamentals
Claisen Condensation:
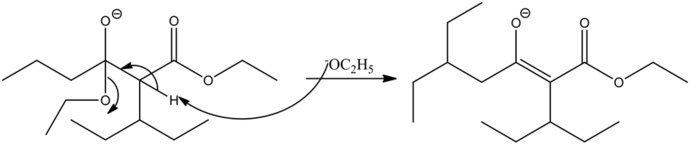
Most commonly, the base used in the claisen condensation reaction is alkoxide,![]() .The ester, on reaction with the base, forms an ester enolate which again reacts with another molecule of ester.
.The ester, on reaction with the base, forms an ester enolate which again reacts with another molecule of ester.
Enolate is a good nucleophile and ester carbonyl carbon is electrophilic in nature.
The final product of this reaction is a beta-ketoester.
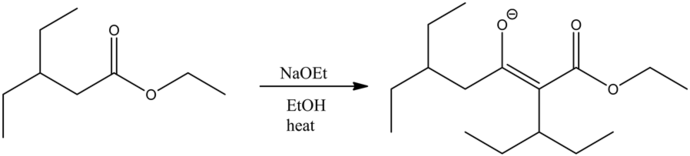
The overall scheme of claisen condensation is as follows:
Aldol condensation:
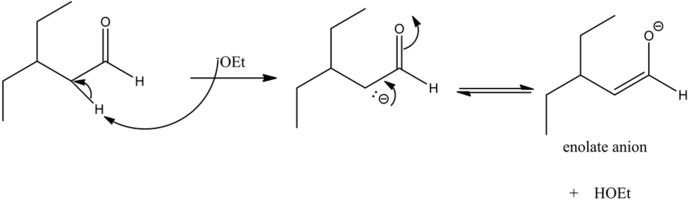
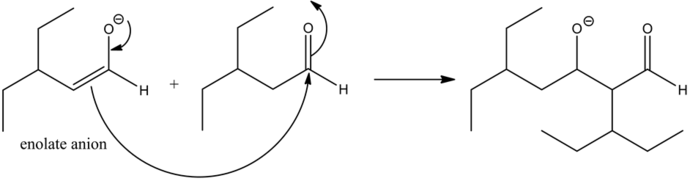
The mechanism of an aldol condensation contains two steps. The first part is an aldol reaction; the second part is a dehydration elimination reaction. First, the base abstracts the proton to form a carbanion. Then, it attacks the carbonyl group of another compound to form an oxy anion. This compound undergoes hydrolysis and forms an aldol, followed by dehydration which will give an aldol product.
Mechanism:-
Answer:
The base abstracts the alpha hydrogen atom of the ester, forming a carbanion. The carbanion donates its electrons to form a highly resonance-stabilized enolate anion. Enolates are very strong nucleophiles.
Enolates are very strong nucleophiles and the carbon atoms of ester carbonyls are very strong electrophiles in nature. Hence, the nucleophilic carbon atom from the ester enolate attacks the electrophilic carbonyl carbon, giving a condensed product.
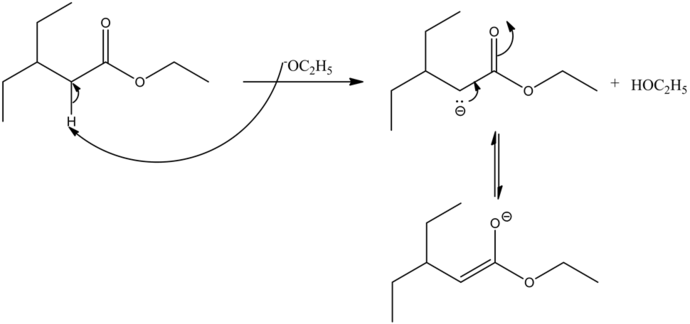
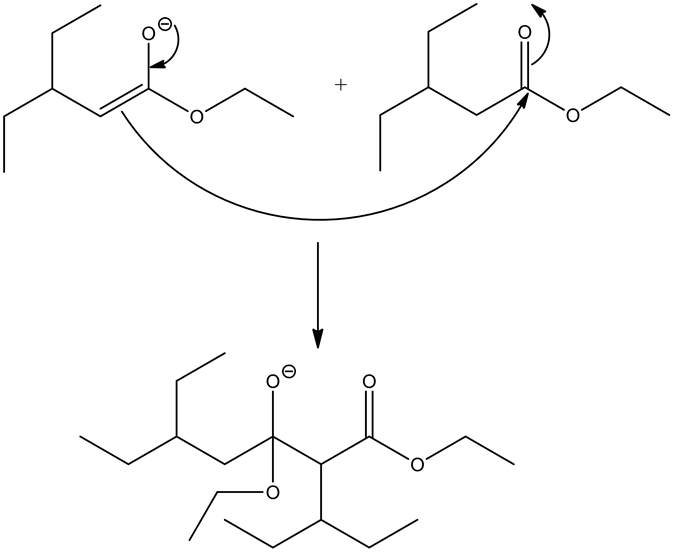
Part a
The most stable product of the given reaction is:
The reaction is base catalyzed. Under a basic medium, the departure of the ethanol group occurs by abstracting the most acidic alpha hydrogen with respect to the carbonyl carbon by the base. Hence, an enolate ion is formed as the final product. Ethanol is a solvent used in this reaction. It does not get involved in the reaction mechanism.
The base abstracts the alpha hydrogen atom of the aldehyde forming a carbanion. The carbanion donates its electrons to form a highly resonance-stabilized enolate anion. Enolates are very strong nucleophiles.
Enolates are very strong nucleophiles and the carbon atoms of carbonyls are good electrophiles in nature. Hence, the nucleophilic carbon atom from the enolate attacks the electrophilic carbonyl carbon giving a condensed product.
Part b
The most stable product formed in the reaction is:
The reaction of the alkoxide with a protonated base gives the aldol condensation product between two aldehydes. The dehydration of the aldol product occurs since there is an alpha hydrogen atom present, with respect to the carbonyl group.