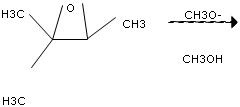
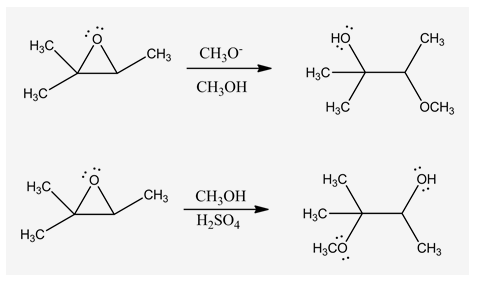
Draw the major product formed in the following reaction of an epoxide with methoxide in methanol.
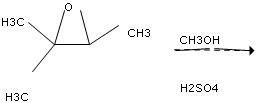
Draw the major product formed in the following reaction of an epoxide with acidic methanol.
Concepts and reason
The three-membered cyclic ring containing 2 carbon atoms and 1 oxygen atom is represented as an epoxide. Epoxides are also known as cyclic ethers. The opening of an epoxide follows an ![]() attack. An epoxide ring opening depends on the type of nucleophile present.
attack. An epoxide ring opening depends on the type of nucleophile present.
Fundamentals
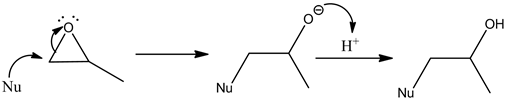
In the presence of a weak nucleophile, the nucleophile attacks an epoxide on its more substituted site and follows a ![]() type reaction. An example for a weak nucleophile is
type reaction. An example for a weak nucleophile is ![]() .
.
Example:
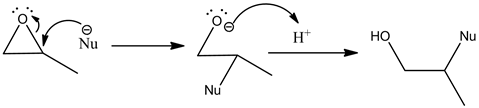
In the presence of a strong nucleophile, the nucleophile attacks an epoxide on a less substituted site and follows a ![]() type reaction. An example for weak nucleophile is
type reaction. An example for weak nucleophile is ![]() .
.
Example:
Answer:
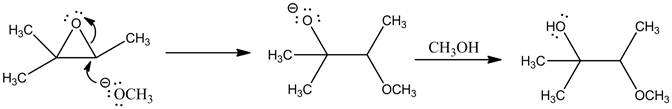
Explanation:
Methoxide ion is a strong nucleophile and it attacks in less substituted site. The opening of epoxide ring takes place and abstracts proton to form an alcohol product.
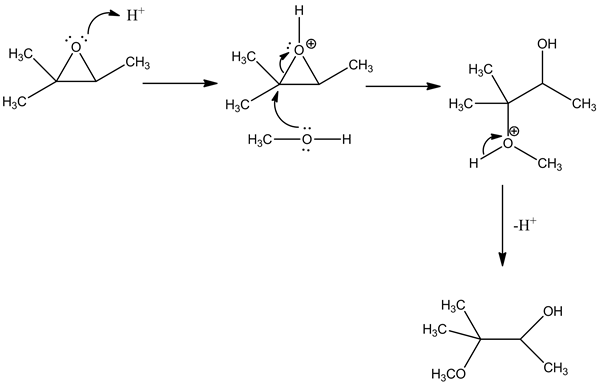
Explanation:
In this reaction, the lone pair electrons of oxygen in the epoxide undergo protonation by an acid. As methanol is less nucleophilic, it attacks the epoxide in a more substituted site and opens the epoxide ring by stabilizing the cation. Then, the cation in oxygen is stabilized by the cleavage of a hydride ion.