Determine the balanced chemical equation for this reaction. C8H18(g)+O2(g)→CO2(g)+H2O(g)
Part A:
Enter the coefficients for each compound in order, separated by commas. For example, 1,2,3,4 would indicate one mole of C8H18, two moles of O2, three moles of CO2, and four moles of H2O.
2,25,16,18
Part B:
0.280 mol of octane is allowed to react with 0.630 mol of oxygen. Which is the limiting reactant?
Oxygen
Part C:
How many moles of water are produced in this reaction?
![]()
Part D:
After the reaction, how much octane is left?
Concepts and reason
Balance the equation by placing appropriate coefficients before the reactant and products. Then write the coefficients that present before the each compound.
Use mole ratio concept to find the limiting reagent. Moles of one substance to moles of another substance in a balanced chemical equation is called mole ratio.
Calculate the number of moles of water by using the moles of the limiting reagent.
Fundamentals
In a balanced chemical equation, number of atoms of each element and total in the reactant side and product side are equal to each other.
A limiting reagent is completely consumed in a chemical reaction.
A conversion factor is used to convert between moles of one substance to moles of another substance.
Answer:
Part A:
The balanced equation is as follows:
![]()
The coefficients of the each compound in order are 2, 25, 16, and 18.
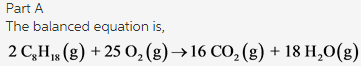
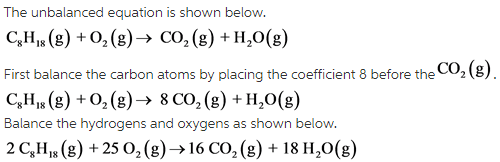
Part B:
Calculate number of moles of ![]() by using the moles of each reactant.
by using the moles of each reactant.

The reactant oxygen produce less product compared to the reactant octane. So, the limiting reagent is ![]() .
.
Part B
Limiting reagent is ![]() .
.
Compare the moles calculated by using the reactants oxygen and octane. Limiting reagent is one that has less number of moles compared with the other reactants in the reaction. The reactant ![]() . less number of moles, hence it will be the limiting reagent.
. less number of moles, hence it will be the limiting reagent.
Part C:
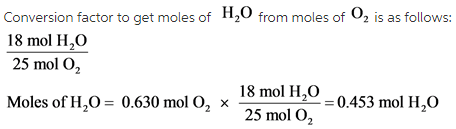
![]()
The reactant for which we calculate moles should be on the top of the conversion factor.
Moles of ![]() should be on the top of the conversion factor. The calculated moles of
should be on the top of the conversion factor. The calculated moles of ![]() is 0.453 mol.
is 0.453 mol.
Part D:
Calculate moles of octane reacted by using the following conversion factor.
Conversion factor to get moles of octane from moles of octane is as follows:
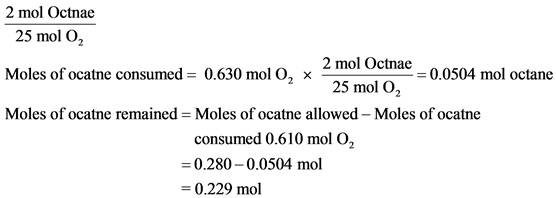
Part D
Amount of octane left is 0.229mol.
The reactant for which we calculate moles should be on the top of the conversion factor.
Moles of octane should be on the top of the conversion factor. Calculate the amount of octane remained by subtracting the moles of octane consumed from the moles of octane allowed in the reaction.
The calculated mole of octane left in the reaction is 0.229mol.
