Consider this reaction and its rate law.
3A + 2B --> products
rate = k[A][B]
What is the order with respect to A?
What is the order with respect to B?
What is the overall reaction order?
Concepts and reason
The concept used to solve this problem is based on the rate law of a chemical reaction.
In a chemical reaction, the rate of reaction depends on the concentration of reactants present in rate law. The rate law is determined by slowest step of the reaction.
Fundamentals
For a chemical reaction in which reactants A and B react to form products,

Answer:
(1)
The chemical reaction is written as follows:
![]()
The rate of reaction is written as follows:
![]()
Thus, the order of reaction with respect to A is 1.

Explanation:
The rate law is written as product of rate constant and concentrations of reactants raised to power their stoichiometric coefficient. The power of concentration of A in the rate law is one. Thus, order of the reaction with respect to A is one.
(2)
The chemical reaction is written as follows:
![]()
The rate of reaction is written as follows:
![]()
Thus, the order of reaction with respect to B is 1.
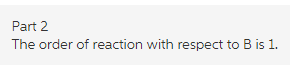
Explanation:
The power of concentration of B in the rate law is one. Thus, order of the reaction with respect to B is one.
(3)
The chemical reaction is written as follows:
![]()
The rate of reaction is written as follows:
![]()
Thus, the overall reaction order is 2.
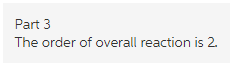
Explanation:
The sum of power of concentration of A and B in the rate law is 2. Thus, order of overall reaction is 2.