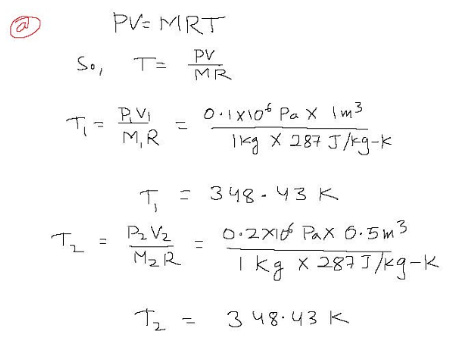
PV = MRT
Where P is V is volume, M is mass, T is arxi R is the specific gas constant, which is equal to 287 J/kg-K for air.
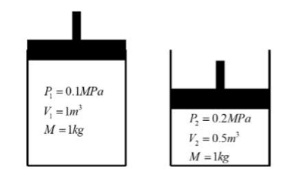
Consider the piston-cylinder diagram below in State I and State 2, where the mass Of air inside cylinder is the same in both
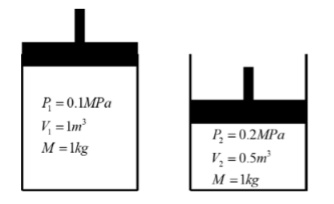
a. Given the information at State 1, what is the temperature ofthe air in State 2?
b. What types of energy transfer proceses were involved in going from State 1 to 2?
What types of energy are important to consider in this example?
Answer:
piston-cylinder thermodynamics