Compare the stabilities of O2 , O2-,O22- .
The stabilities of these can be best explained using Molecular orbital theory.
(i) Formation Oxygen molecule:
Electronic configuration of oxygen atom-1s² 2s² 2p⁴
Atomic orbitals of oxygen combine to form molecular orbitals.
BO = bonding orbitals
ABO = Anti-bonding orbitals
O2 :
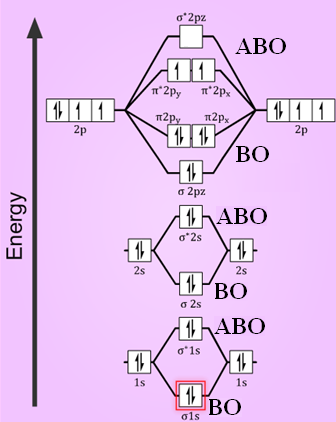
Electronic configuration of Oxygen molecule =
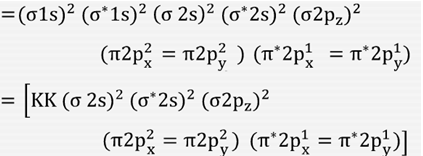
Bond order in Oxygen molecule (O2)=
=½ [(Number of bonding electrons) – (number of anti-bonding electrons)]
= ½ [10 – 6]
= 2
O2- :
Bond order in Oxygen molecule (O2-)
=½ [(Number of bonding electrons) – (number of anti-bonding electrons)]
= ½ [10 – 7]
= 1½
O2-2 :
Bond order in Oxygen molecule (O2-2)
=½ [(Number of bonding electrons) – (number of anti-bonding electrons)]
= ½ [10 – 8]
= 1
With the increase in number of electrons in anti-bonding orbital the stability and bond order of the molecule decreases.
Thus Decreasing order of stability is: O2 > O2- > O2-2

