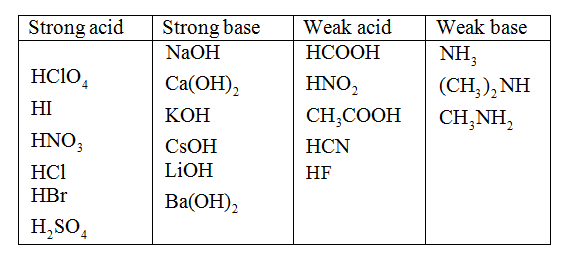
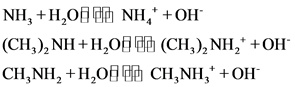Classify each substance as a strong acid, strong base, weak acid, or weak base.
- HCCOH
- HClO4
- HI
- NH3
- NaOH
- HNO2
- CH3COOH
- (CH3)2NH
- HNO3
- Ca(OH)2
- HCl
- KOH
- HCN
- HF
- CH3NH2
- CsOH
- HBr
- LiOH
- Ba(OH)2
- H2SO4
Concepts and reason
The acidic strength depends on the electronegativity of the hydrogen bonded carbon atom. If electronegativity of the carbon atom increases, the acidic strength of that compound increases.
The basic strength depends on the strength of its conjugate acid; if the conjugate acid is more acidic, then the carbanion is less basic.
Fundamentals
Electronegativity: The tendency to attract the bonded pair of electrons towards one atom is called the electronegativity of that atom. Electronegativity of an atom can also be explained through the percentage of S-character present in its hybridized orbital.
If the s-character present in hybridized orbital is more, electronegativity will be more for that atom.
According to the Lewis acid base theory,
oElectron donors are base
oElectron accepters are acid.
Answer:
The strong acids are as follows:
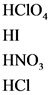
Explanations:
The above compounds are strong acid. When these compounds are dissolved in water, they dissociate completely and give hydronium ions and their corresponding anions.
Strong acid completely dissociate and gives hydronium ion
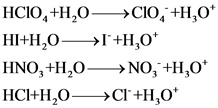
The weak acids are as follows:
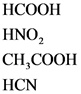
Explanations:
The above compounds are weak acids. When these compounds are dissolved in water, they dissociate partially and give hydronium ions and their corresponding anions. Since the HF is a weak acid, due to the fluorine it is more electronegative and does not easily release proton.
Weak acid partially dissociate and gives hydronium ion
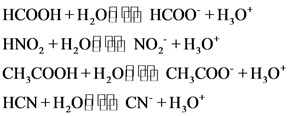
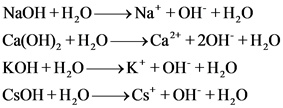
The strong bases are as follows:

Explanations:
The above compounds are strong base. When these compounds are dissolved in water, they dissociate completely and give hydroxide ions and their corresponding cations.
Strong bases completely dissociate and gives hydronium ion
The weak bases are as follows:
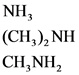
Explanations:
The above compounds are weak bases. When these compounds are dissolved in water, they dissociate partially and give hydroxide ions and their corresponding cations.
A weak base partially dissociates and gives hydronium ion