(a) List two reasons for the appearance of variations among the progeny formed by sexual reproduction.
(b) 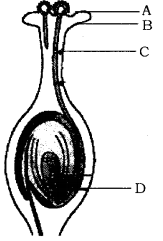
- Name the part marked ‘A’ in the diagram.
- How does ‘A’ reaches part ‘B’?
- State the importance of the part ‘C’.
- What happens to to the part marked ‘D’ after fertilisation is over?
(a) Appearance of variations among progeny is due to mixing of genes alleles provided by
both parents. Parents produce gametes. They fuse together to form zygote and genetic variability occurs in progeny. Zygote is formed by new Combination of variants.
(b) A = Pollen grain : They are male reproductive strictures and form male gametes.
B = Style stigma : Pollen grains land and germinate here.
C = Pollentube : Pollen tube emerges from pollen and grows down style towards ovary.
D = Female gamete : It fuses to male gamete to form a zygote.
