(a) Define the following terms in the context of spherical mirrors:
- Pole
- Centre of curvature
- Principal axis
- Principal focus
(b) Draw ray diagrams to show the principal focus of a :
- Concave mirror
- Convex mirror
(c ) Consider the following diagram in which M is a mirror and P is an object and Q is its
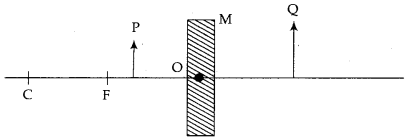
State the type of the mirror M and one characteristic property of the image Q.
(a) 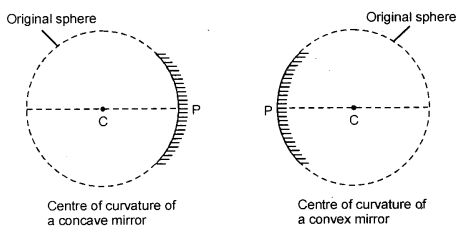
- Pole: The middle point of the reflecting surface of a spherical mirror is called pole.
The letter P represents pole, MP = M’P.
- Centre of curvature: It is the centre of the sphere of glass of which the mirror is a part. The letter C represents the centre of curvature.
- Principal axis of a spherical mirror is the straight line joining the centre of curvature and pole of the mirror.
- Principal focus: The mid-point of CP is called focus (F). It is the point on the principal axis of a spherical mirror where all incident rays parallel to the principal axis meet or appear to diverge after reflection.
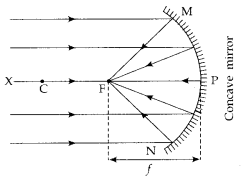
(b) Ray diagrams of principal focus:
- Concave mirror : In a concave mirror the reflected rays of incident rays parallel to principal axis actually pass through the focus (F). Thus, concave mirror has a real principal focus.
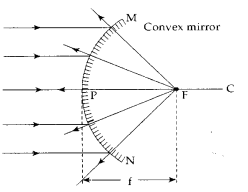
- Convex mirror : In a convex mirror the reflected rays do not actually pass through the focus (F). Thus, a convex mirror has a virtual principal focus situated behind the mirror.
(c ) The mirror used in the given diagram is a concave spherical mirror. Image formed (Q) is virtual and magnified.



