A coil of insulated copper wire is connected to a galvanometer. What will happen if a bar magnet is
(i) pushed into the coil
(ii) withdrawn from inside the coil
(iii) held stationary inside the coil? Name the phenomenon involved in the above cases.
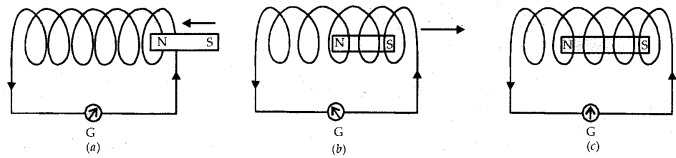
(i) When a bar magnet is pushed into the coil, induced current flows through the coil due to the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction. This induced current is indicated by the deflection of the needle of the galvanometer as shown in figure (a).
(ii) When a bar magnet is withdrawn from inside the coil, again induced current flows through the coil due to the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction. In this case, the direction of induced current is opposite to the direction of the current in case (i) shown in figure (b).
(iii) When the bar magnet is held stationary inside the coil, there is no change in magnetic field around the coil. Hence, no induced current flows through the coil. Therefore, galvanometer shows no deflection as shown in figure (c ).
Phenomenon involved is Electromagnetic Induction.