A. Calculate the pH of a 0.10 M solution of barium hydroxide, Ba(OH)2.
B. Calculate the pH of a 0.10 M solution of NaOH.
C. Calculate the pH of a 0.10 M solution of hydrazine, N2H4. Kb for hydrazine is 1.3
Concepts and reason
For strong bases, the pOH of the solution can be calculated directly from the concentration of the solution using the following formula:
![]()
The relationship between pH and pOH is ![]() .
.
Fundamentals
For strong bases or acids, 100% ionization takes place. Hence, from the concentration of the base, the concentration of hydroxyl ion can be calculated.
For weak bases or acids, 100 % ionization does not take place. Hence, for weak acids or bases, the concentration of hydroxyl ion can be calculated using the equilibrium expression.
Answer:
Part A
The reaction is as follows:

Therefore, the pH of a 0.10 M barium hydroxide solution is 13.3.
Part B
The reaction is as follows:
![]()
One mole of NaOH gives one moles of ![]() ions.
ions.
It is given that the concentration of NaOH solution is 0.10 M.
Hence, the concentration of ![]() ions is 0.010 M.
ions is 0.010 M.

Therefore, the pH of a 0.10 M sodium hydroxide solution is 13.
As sodium hydroxide is a strong base, 100% ionization takes place. The concentration of NaOH solution is equal to the concentration of ![]() ions.
ions.
Part C
The reaction is as follows:

Now, calculate the concentration of ![]() from the equilibrium expression as follows:
from the equilibrium expression as follows:
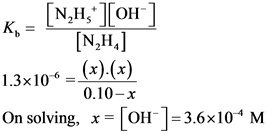
Therefore, the pH of a 0.10 M hydrazine solution is 10.56.
Hydrazine is a weak base. Very small fraction of the molecules dissociates into ions. Hence, for weak bases, the concentration of the solution is not equal to the concentration of hydroxyl ion.