Predict the organic product of the following reactionsand include hydrogen atoms in your structure.
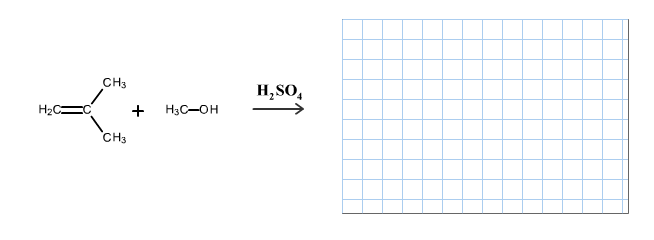
Concepts and reason
This problem is based on the concept of acidic hydration and hydrohalogenation of alkenes.
Alkenes have high electron density due to the presence of pi-bond. As a result, alkenes are highly reactive towards the chemical species which are electron deficient in nature such as acids.
Fundamentals
In the reaction of alkenes with acids, alkenes attacks on the acids in order to get protonated which results in the formation of the most stable cation and then the chemical species having high electron density attacks on this cation.
Answer:
Part A
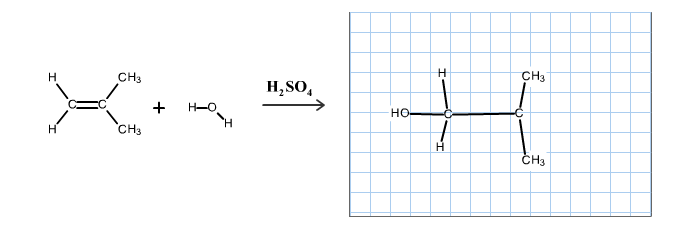
The reaction is alkene is with the sulfuric acid (protonation) is given below:
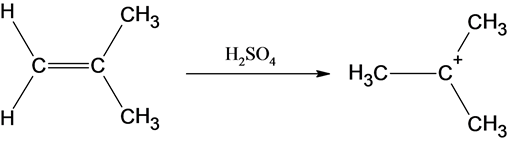
This reaction follows the Markovnikov’s rule which states that the hydrogen atom will be added to the olefinic carbon having more number of hydrogens in order to form most stable carbocation.
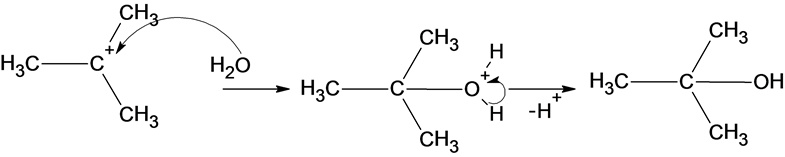
The reaction of carbocation with water molecule is given below:
Part a
The structure of the product is as follows:
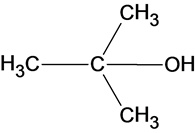
In the reaction water molecule attacks on the carbocation and forms an oxonium ion which on deprotonation result in the formation of a tertiary alcohol.
Part B
The reaction is alkene is with the sulfuric acid (protonation) is given below:
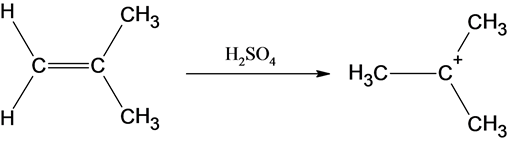
This reaction follows the Markovnikov’s rule which states that the hydrogen atom will be added to the olefinic carbon having more number of hydrogens in order to form most stable carbocation.
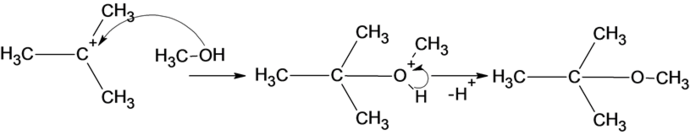
The reaction of carbocation with methanol is given below:
Part b
The structure of the product is given below:
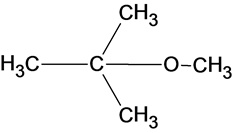
In the reaction methanol molecule attacks on the carbocation and forms an oxonium ion which on deprotonation result in the formation of an ether.
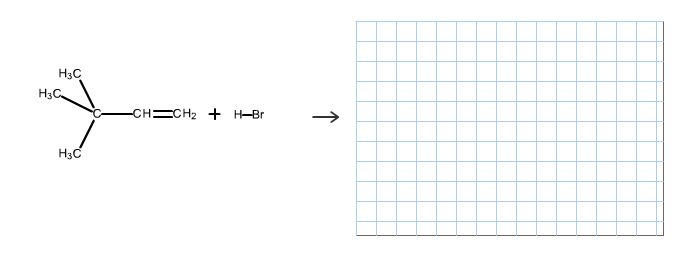
Part C
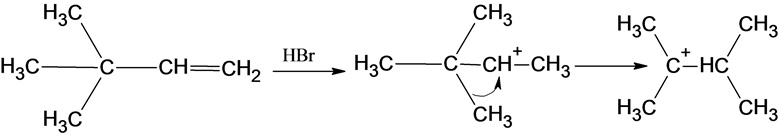
The reaction is alkene is with the hydrogen bromide (protonation) is given below:
This reaction follows the Markovnikov’s rule which states that the hydrogen atom will be added to the olefinic carbon having more number of hydrogens in order to form a secondary carbocation which rearranges to tertiary carbocation because tertiary carbocation is more stable.
The reaction of carbocation with bromide ion is given below:
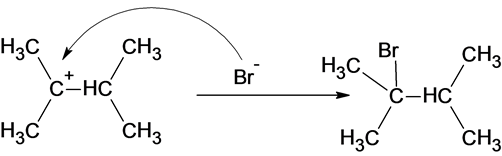
Part c
The structure of the product is as follows:
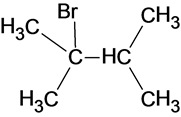
In this reaction, bromide ion attacks on the tertiary carbocation and forms a carbon halogen bond in order to form a bromoalkene.