In an experiment, the specific heats of some inert gases (at ordinary temperature) one measured to be as follows:
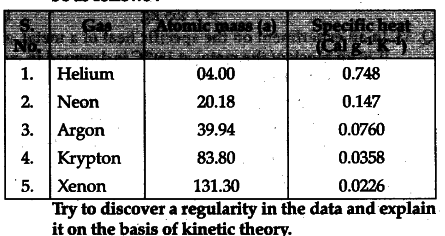
. If we multiply atomic mass by sp. heat, we get 2.99, 2.94, 3.03,3.00,2.97 respectively for the gases given in the table. This shows the product of the molecular mass ( = atomic mass for the above rqpnoatomic gases) and specific heat is approximately equal to 3 cal = 3/2 R.
This is the result expected from kinetic theory of gases because monoatomic gas particle will have 3 degree of freedom and the energy per mole of such a gas = 3/2 R = 3 cal