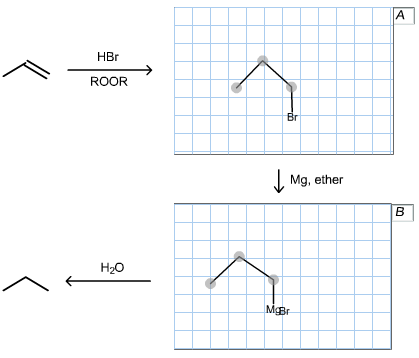
Draw the structures of organic compounds A and B, Omit all by products.
Concepts and reason
- Hydro halogenation: An addition of hydro halogen to an unsaturated compound is known as hydro halogenation.
- Hydration: An addition of water molecule to the substrate is known as hydration process. Sometimes, Grignard reagent may act as substrate to give pure alkane.
- Metal incretin: Metals are inserted between the alkyl group and halogen in the presence of ether as solvent.
Fundamentals
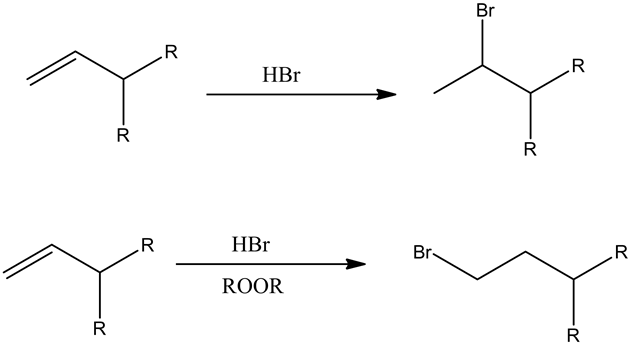
Hydro halogenation: An addition of hydrogen halide across the double bond of the substrate is known as hydro halogenation, this process could happen in either Markovnikov’s path or anti-Markovnikov’s path.
If the reagent is only HBr, then Markovnikov’s addition occurs, if the reagent is HBr in the presence of peroxide, then anti-Markovnikov’s addition occurs.
Hydration: Hydration of Grignard reagent is ended up with alkane giving magnesium hydroxy bromide as a product.
![]()
Answer:
The given substrate is drawn below:
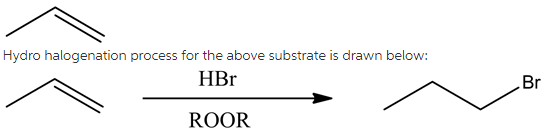
The given reagent in the reaction is HBr in the presence of peroxides, which follows radical mechanism and gives anti-Markovnikov’s product. In this reaction, bromine atom will attach to the least substituted carbon position while hydrogen atom is attached to the most substituted carbon atom.
Alkyl halide structure is drawn below:
![]()
Reaction between the propyl bromide and magnesium (metal) is drawn below:
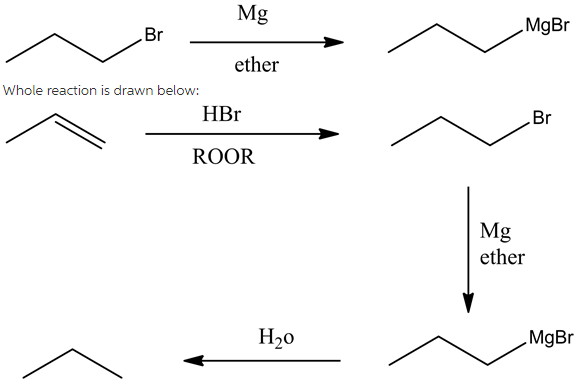
It is clear that the substrate and the reagent conditions represent the metal insertion reaction, where Mg (magnesium) is the metal inserted between alkyl and halogen atom in the alkyl halide.