Write notes on:
- Adam’s apple.
- Secondary sexual characters.
- Sex determination in the unborn baby.
Answer:
- Adam’s apple: In human males, the larynx grows larger during puberty and
can be seen as a protruding part of the throat. This protrusion is known as the Adam’s apple. In boys, under the influence of sex hormones, the larynx becomes prominent. As a result, the vocal cords become longer and thicker, causing the voice to become hoarse.
However, in females, the larynx is of a small size and is hardly visible. Therefore, girls have a high-pitched voice, while the voice of boys is low- pitched. - Secondary sexual characters are those features that help in distinguishing the male and the female body from each other. They are physical or behavioural characteristics that appear in humans at the time of puberty.
Secondary sexual characters in boys:
- Appearance of moustache and beard.
- Appearance of chest hair.
- Growth of hair in genital area and other parts of the body.
Secondary sexual characters in girls:
- Increase in breast size and darkening of the skin of nipples present at the tip of the breasts.
- Growth of hair in genital area and other body parts.
3. Sex determination in an unborn baby:
The sex of a baby is determined by the type of male gamete that fuses with the female gamete.
All human beings have 23 pairs of chromosomes in their nuclei. Out of these 23 pairs, the last pair is known as the sex chromosome. ’
The human males have 23 pairs of chromosomes including XY sex chromosomes. Therefore, the male gamete has 22 chromosomes and either an X or Y sex chromosome.
Male gametes can be of two types: 22 + X or 22 +Y
Females have 23 pairs of chromosomes including XX sex chromosomes. Therefore, their gametes can only have 22 chromosomes and one X sex chromosome.
Type of female gametes: 22 + X
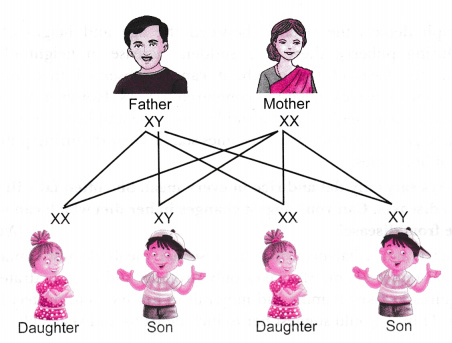
Thus, as the mother provides only X chromosome, the sex of the baby is determined by the type of male gamete (X or Y) that fuses with the X chromosome of the female.