At a given price of a commodity, there is excess supply. Is this an equilibrium price? If not, how will the equilibrium price be reached?
Equilibrium price refers to the price at which market demand is equal to market supply (i.e. there is no excess demand or excess supply).
No, the price with excess supply is not an equilibrium price. This can be illustrated with the help of following diagram:
In the given figure, excess supply is equal to = {{Q}_{1}}
{{Q}_{2}} AB.
It implies market supply is greater than market demand. This puts pressure on price ({{OP}_{1}}) to decline.
The producers reduce the quantity supplied at the lower price (OP) from {{OQ}_{2}} to OQ with declining price. The consumer reacts by increasing the quantity demanded equilibrium is struck at point E.
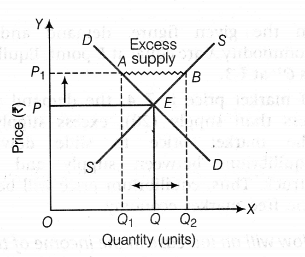
Thus, OP and OQ are the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity respectively with no excess supply.